CONTENTS :
- Boiler fundamentals
- Heat recovery boiler
- Boiler operation
- Boiler maintenance
- Boiler risk factor
- Precaution & safety
Boiler:
A boiler is an enclosed vessel made of steel in which water is heated by combustion of flue gases or exhaust and circulated, either as hot water, steam, or superheated steam for the purpose of heating, powering, and/or producing electricity.
Types:
- Fire tube or smoke tube boiler
- Water tube boiler
Fire tube boiler:
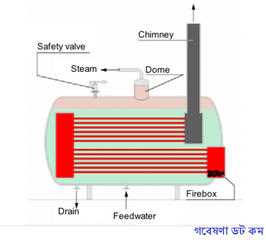 In fire tube steam boilers, the flames and hot gases pass through the tubes which are surrounded by water. Fire tube boilers are generally used for relatively small steam capacities and low & medium steam pressure. As a guideline, fire tube boilers are competitive for steam rates up to 12000kg/h and pressures up to 18 kg/cm² (18 Bar). Fire tube boilers are available for operation with oil, gas or solid fuel.
In fire tube steam boilers, the flames and hot gases pass through the tubes which are surrounded by water. Fire tube boilers are generally used for relatively small steam capacities and low & medium steam pressure. As a guideline, fire tube boilers are competitive for steam rates up to 12000kg/h and pressures up to 18 kg/cm² (18 Bar). Fire tube boilers are available for operation with oil, gas or solid fuel.
Water tube boiler:
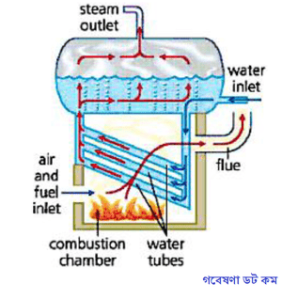
In Water tube boilers, the water is contained inside the tubes which are surrounded by flames and hot gases from outside. The steam capacity of boiler range 4500- 120000kg/h at very high pressure Example: Babcock and Wilcox boiler, Sterling boiler, La Mont boiler, Benson boiler.
Exhaust Gas/Heat Recovery Boiler :
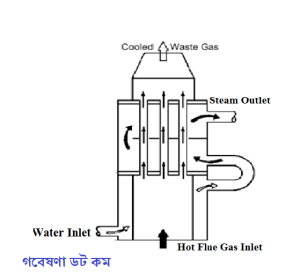
An Exhaust Gas Boiler is a type of heat recovering system which allows the exhaust heat of the main engine, such as hot flue gases from a DG/GG to produce steam while going out in the atmosphere.
Advantages Of EGB:
- Decrease the costs of fuel and energy consumption needed for that process.
- Thermal and air pollution will dramatically decrease since less flue gases of high temperature are emitted from the plant.
- As Fuel consumption reduces so the control and security equipment for handling the fuel decreases.
- Reduction in equipment sizes means another reduction in the energy fed to those systems like filters, fans…etc.
Disadvantages of EGB:
- The capital cost to implement a waste heat recovery system may outweigh the benefit gained in heat recovered.
- Often waste heat is of low quality (temperature). Heat exchangers tend to be larger to recover significant quantities which increases capital cost.
- Need to shutdown the exhaust generating like GG or DG unit which create major breakdown of plant.
Important Terms:
- Boiler shell:It is made up of steel plates bent into cylindrical from reverted or welded together.
- Combustion chamber:It is the space generally below the boiler shell, meant for burning fuel in order to produce steam from the water contained in the shell.
- Gate:It is the platform in the combustion chamber, upon which fuel is burnt. The surface are of the gate over which the fire takes place is called gate surface.
- Furnace:It is the space above the gate and the boiler shell in which the fuel is actually burnt the furnace is also called fire box.
- Heating surface:It is that part of boiler surface which exposed to the fire.
Different Parts of a Boiler:
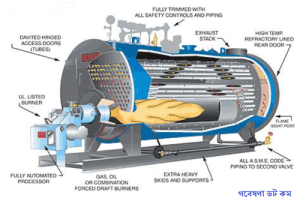
Water indicator: It is an important fitting which indicate the water level inside the boiler.
Pressure gauge: A pressure gauge is used to measure the pressure of the steam boiler.
Safety valves: There are the devices attached to the steam chest for preventing explosions due to excessive internal pressure of steam.
Stop valve: It is the largest valve on the steam boiler. It is used to control the flow of steam from boiler to the main steam pipe.
Blow off cock: It is fitted to the bottom of a boiler drum and its function is to empty the boiler whenever required and to boiler bottom discharge the mud, scale or sediments.
Feed check valve: It is a non-return valve fitted to a screwed spindle to regulate the lift.
Fusible plug: It is fitted to the crown plate of the furnace or the fire. Its object is to put off the fire in the furnace of the boiler when the level of water in the boiler falls to an unsafe limit and thus avoids the implosion which may take place due to overheating of the furnace plate.
Blow down valve: It is fitted to the lower side of the boiler. Its function is to reduce the impurities of the boiler.
Boiler Accessories:
Feed pump:
A feed pump needed to deliver water to the boiler. The pressure of feed water is 20% more than that in the boiler. The feed pump may be classified as simplex, duplex, triplex pumps according to the number of pump of cylinder.
Super heater:
A super heater is an important device of a steam generating unit. Its purpose is to increase the temperature of saturated steam without raising its pressure. It is generally an integral part of a boiler and is placed in the path of hot flue gases from the fluency. The heat given up by these flue gases is used in super heating the steam.
Economizer:
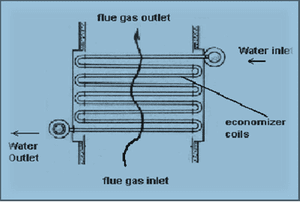
An Economizer pre-heater is used to recover heat from the exhaust flue gases. It is installed between the economizer and chimney. The air required for the purpose of combustion is drawn through the air pre-heater where its temperature is raised. There is an increase of about 2% in the boiler efficiency for each 35-40% raise in temperature of air.
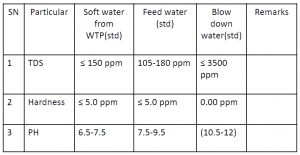
Water Quality of Boiler:
As with all systems where water is heated there will be a potential for scaling. This can lead to a loss of efficiency or, in extreme cases, premature failure of the boiler due to either scale build-up on the internal surfaces or debris from corrosion collecting in the bottom of the boiler.
Bore-well water normally contains calcium, magnesium, iron, manganese which increase the hardness of water. It causes the scaling in boiler. That’s why softener required.
Following water parameter need to maintain.
Troubleshooting:
Boiler Fails to Meet System Load:
(a)Cause: the boiler thermostat is set incorrectly.
Corrective action: is to check the thermostat setting.
(b)Cause: poor combustion.
Corrective action: check flue, flame, and assess combustion quality.
Boiler and System Overheat:
(a) Cause: system controls are faulty.
Corrective action: is to check voltage, temperature settings, and safety switches.
(b) Cause: The control thermostat failed and high-limit thermostat activated, or both controls may have failed. Corrective action: to be taken is to check temperatures if they are higher than the high-limit set point, replace the high-limit thermostat.
Fumes in Boiler Room:
(a) Cause: incorrect combustion.
Action: Perform a combustion analysis and correct.
(b) Cause: Inadequate airflow for combustion.
Action: inspect the boiler, chimney, and boiler room fresh air intake for the source of the blockage.
(c) Cause: test holes in the flue that are unsealed or flue leakage.
Action: To correct, cover the holes and check for leakage.
Boiler Does Not Ignite:
(a) Cause: Check for a boiler internal controls failure.
Action: Investigate this possibility and reset or replace.
(b) Cause: The boiler may have previously overheated and the overheat cut-out has not reset.
Action: Determine the cause of the overheat condition. Once it has been corrected, reset.
(c) Cause: The supply fuse may have blown or the supply isolated.
Action: Establish the cause of the blown fuse and replace.
d) Cause: There may no pilot flame.
Possibilities for this condition are:
(1) a dirty or incorrectly installed pilot nozzle (2) insufficient gas supply to pilot (3) pilot flame ignites but becomes faulty (4) thermocouple voltage is too low.
Boiler Fires Continuously:
(a) Cause: is a thermostat fault.
Action: Investigate and either repair or replace the thermostat.
(b) Cause: There could be a wiring fault.
Action: Check the wiring and make the required repair.
(c) Cause: control valve that is faulty or sticking.
Action: Replace the valve.
Boiler Overheats and Is Noisy:
(a) Cause: There could be poor circulation in the primary circuit.
Action: Vent the system.
(b) Cause: Low shunt-pump discharge pressure.
Action: Open a piping joint and check for foreign materials. There may be an air pocket in the line; purge the system.
Boiler Starts but Flame Goes Out Soon After:
(a) Cause: Flue blockage.
Action: Check the flue for blockage. Check dilution fan operation.
(b) Cause: Primary low-pressure hot water (LPHW) circuit failure.
Action: Check operation of the high-temperature cut-out.
Fault in Flue Gas System:
(a) Cause: May be that the flue gas fan does not run during the start sequence.
Action: Check the control circuit.
(b) Cause: Fan has stopped during operation.
Action: Check the fan, make any necessary fixes, and restart.
Boiler Safety:
Boiler Over Heating:
An overheating boiler may exhibit the following conditions:
- A discharging safety relief valve.
- Pressure and/or temperature readings above the maximum allowed for the boiler.
- Low or no water in boilers equipped with water-level Gage glasses.
- Scorched or burning paint on the skin casing.
Precaution:
- Do not try to relieve the pressure.
- Do not add cool water into the vessel.
- Do not try to cool the vessel with water.
- Let the vessel cool down naturally.